Making All Data Discoverable: Delta Sharing with MinIO AIStor and Databricks

Enterprises are increasingly living in a hybrid world. Data is distributed across public cloud and private infrastructure and needs to be discoverable everywhere. For organizations that use Databricks’ Lakehouse Platform, the priority is to unify access so that all data can be discovered, governed, and used across the entire enterprise. Delta Sharing with MinIO AIStor extends Unity Catalog’s mission of data unification, connecting Databricks directly to on-prem object storage without unnecessary duplication and ensuring a single, consistent view of enterprise data.
The Hybrid Challenge
Organizations often run into challenges when balancing private and public infrastructure. Public cloud customers rely heavily on SaaS tools like Databricks notebooks and benefit from native integrations with the wider data community. This approach is convenient but tends to overlook on-prem resources. Private cloud customers focus on reducing costs with long-running compute, avoiding API charges, and maintaining freedom to choose their security mode, and preferred storage system.
In many cases, this hybrid setup leads to the mirroring of data between environments, which adds operational complexity. Delta Sharing with AIStor addresses these problems by giving users live access to Delta Lake tables without copying or moving data between systems.
Unity Catalog: A Unified View of All Enterprise Data
Unity Catalog is Databricks’ centralized governance layer for data and AI assets. Its mission is to make all data discoverable, secure, and governed from a single control plane, regardless of where that data lives. Instead of treating cloud and on-premises data differently, Unity Catalog abstracts away infrastructure complexity and gives teams a consistent way to manage permissions, enforce policies, and search for data across multiple environments.
For enterprises operating at scale, Unity Catalog represents a critical step toward data unification. It brings together structured and unstructured data, real-time and batch workloads, and multiple cloud or on-premises storage solutions under a single metadata layer. Combined with Delta Sharing and AIStor, Unity Catalog extends this unified governance model beyond Databricks itself, creating an open and interoperable ecosystem where every dataset is a first-class citizen.
What is Delta Sharing
Delta Sharing is an open protocol designed for secure data sharing across organizational boundaries. It allows teams to access Delta Lake tables directly from their preferred tools. This protocol is designed for scale and supports integration with Spark, Pandas, Rust, Power BI, Tableau, and other tools. It also provides governance controls, auditing, and simple permission management.
By combining Delta Sharing with AIStor, organizations gain a unified data-sharing layer that works seamlessly across cloud and on-prem environments.
How Delta Sharing with AIStor Works
The architecture places the reference Delta Sharing Server in a private cloud environment, secured behind an NGINX reverse proxy. The control plane manages authentication and authorization over HTTPS using bearer tokens, while the data plane provides direct access to data stored in AIStor.
Azure-Databricks already works with this setup where we tested. Client credentials are distributed via JSON files, renamed with a .share extension, which Databricks Unity Catalog can import for secure access.
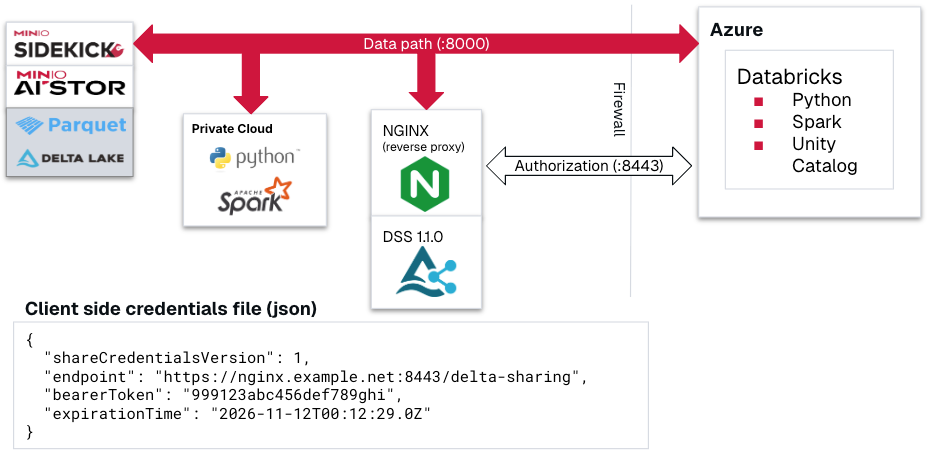
MinIO Sidekick provides an easy solution for load-balancing the client requests to the AIStor cluster - both private and public cloud applications.
Implementation Overview
Setting up Delta Sharing with AIStor begins with a YAML configuration that defines the tables, schemas, and endpoints you want to share. The proxy configuration provides TLS termination and allows you to isolate authentication traffic from data traffic.
version: 1
shares:
- name: "deltatest"
schemas:
- name: "demodata"
tables:
- name: "demo_tbl"
location: "s3a://deltatest/demodata/demo_tbl"
id: "00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000"
host: "nginx.example.net"
authorization:
bearerToken: 999123abc456def789ghi
port: 8080
endpoint: "/delta-sharing"Sample YAML configuration for Delta Sharing Server.
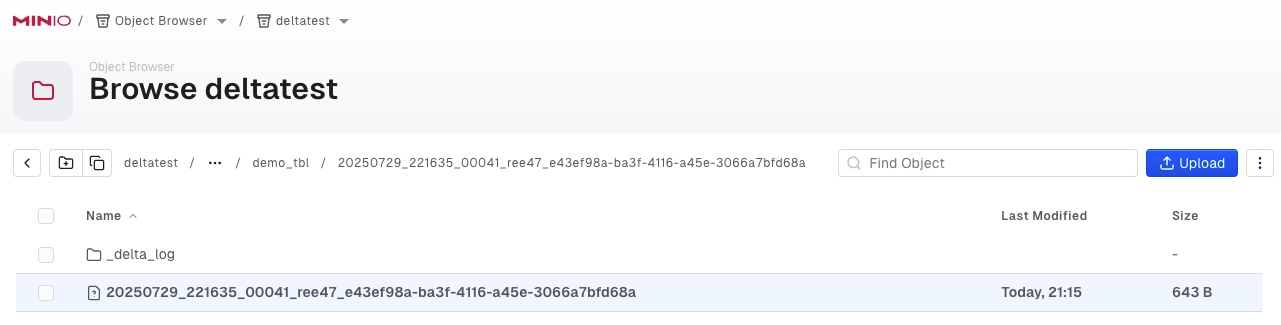
The Delta Tables retrieved from AIStor object storage are located in the bucket path deltatest/demodata/demo_tbl which is the location called out in the Delta Share configuration.
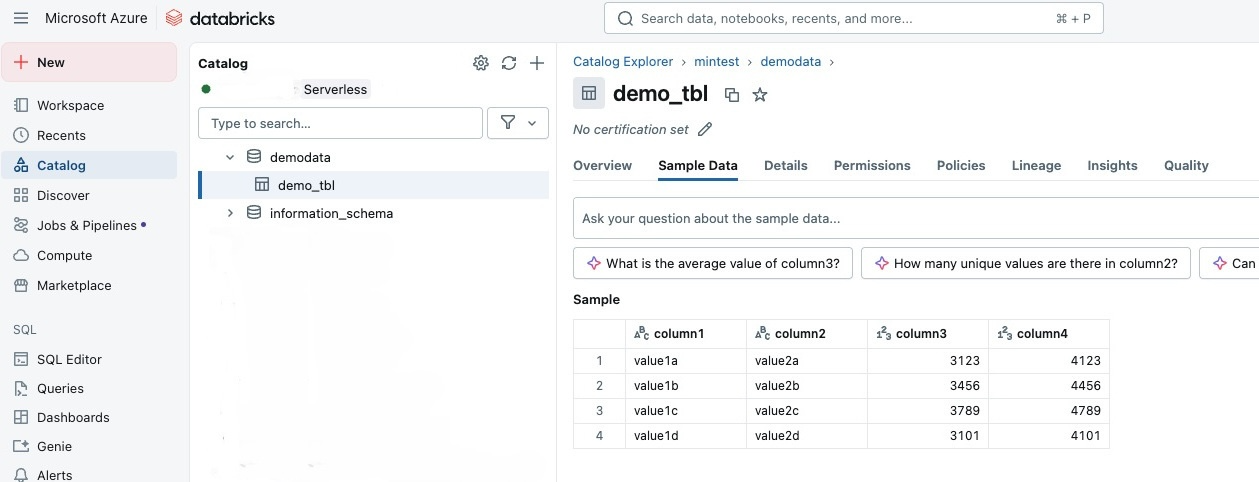
Once deployed, clients can connect using Unity Catalog or Python scripts. Here’s an example of querying a Delta table and displaying results in a pandas DataFrame:
from delta_sharing import SharingClient
import delta_sharing
import pandas as pd
profile_file = "/home/user/mintest-profile.share"
share_name = "deltatest"
schema_name = "demodata"
table_name = "demo_tbl"
try:
client = SharingClient(profile_file)
table_url = f"{profile_file}#{share_name}.{schema_name}.{table_name}"
delta_table = delta_sharing.load_as_pandas(table_url)
print(f"\nFirst 4 rows of the Delta table {table_name}:")
print(delta_table.head(4))
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error reading Delta table: {str(e)}")First 4 rows of the Delta table demo_tbl:
column1 column2 column3 column4
0 value1a value2a 3123 4123
1 value1b value2b 3456 4456
2 value1c value2c 3789 4789
3 value1d value2d 3101 4101
Logs for Auditing and Troubleshooting
Detailed server and storage logs make it easy to monitor performance and investigate issues:
LOG: 15:49:22.993 [200 OK] https://lab03.example.net:9000 GET
/deltatest/demodata/demo_tbl/... 192.168.0.39 3.452ms ↑ 112 B ↓ 1.2 KiB
LOG: 15:49:23.013 [200 OK] https://lab04.example.net:9000 GET
/deltatest/demodata/demo_tbl/... 192.168.0.39 1.933ms ↑ 117 B ↓ 1.2 KiBPerformance and Security Considerations
Performance in a hybrid setup depends heavily on the connection speed between public and private resources. Remote connections should use load balancers or reverse proxies for security. The current implementation supports Delta Lake and Parquet formats and relies on bearer tokens, with plans for OIDC integration. Data masking is currently coarse-grained, and TLS certificates must be carefully managed.
Why It Matters
Delta Sharing with AIStor simplifies hybrid analytics. It eliminates unnecessary data duplication, works with open standards, and performs well with large-scale datasets. For organizations seeking a future-proof architecture, this approach provides a secure, standards-based way to deliver analytics wherever your teams work.
We are looking forward to more community involvement in AWS and GCP deployments with Databricks and their support for Delta Sharing.
Learn More
For further details and implementation guides, explore the following:






